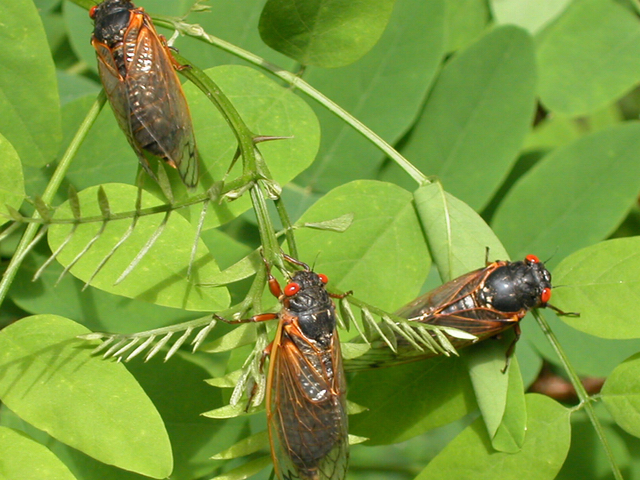
After 17 years underground, billions of Brood X cicadas will emerge and invade the Miami Valley.
The cicadas will find their way to the surface when the ground, eight inches below ground, reaches 64 degrees Fahrenheit, according to the Ohio Department of Natural Resources (ODNR).
This usually occurs between late April and mid-May.
With their arrival just around the corner, ODNR wants to remind people of the importance of trees in a cicada life.
ODNR says that it may be advisable to plant trees and shrubs after the cicadas have disappeared, but that they play a huge role in insect reproduction.
Shortly after surfacing, cicadas climb a vertical surface like tree trunks, shedding their exoskeletons and developing into winged adults.
“Periodic cicadas are noticeable for their sheer numbers and constant cricket-like noise, which is the male ‘singing’ to attract female cicadas,” said Tom Macy, manager of the ODNR division of the Forestry Forest Health Program. “The cicada choir is the loudest natural sound in the world.”
After mating, female cicadas cut slits in the branches and stems of trees and shrubs to lay eggs in the openings, according to the ODNR.
“Cicada egg-laying behavior can kill plant branches from oviposition to the tips of the branches, often causing withered and discolored foliage to become visible in midsummer,” Macy said. “While this branch tip death looks like a major plant health problem, the damage to most plants is negligible.”
ODNR also says that pesticides and repellants on the leafhoppers are ineffective and are not recommended.
If you’ve already planted trees and shrubs for spring, nets or cheesecloths placed over them can protect them from cicada damage, according to the ODNR.